Symptoms
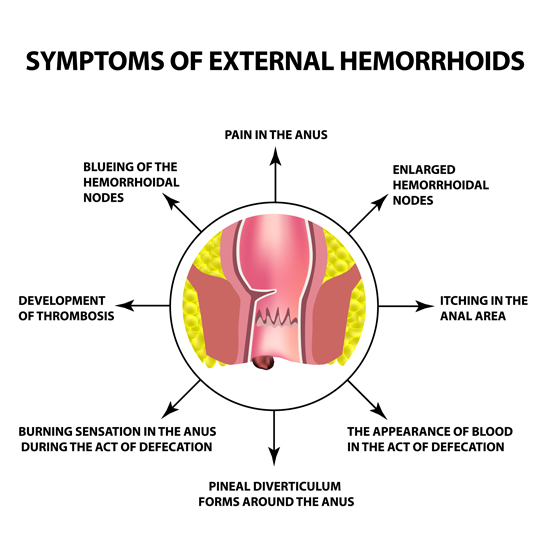
Typical symptoms are bleeding, itchiness or irritation of the anal region, a feeling of pressure and in later stages even fecal incontinence.
Treatment options
Non-surgical treatment is possible at stage 1 and 2 of hemorrhoids. High fiber diet, mild stool softeners, lukewarm sitz baths, salves, and suppositories can help.
Sclerotherapy:
Small hemorrhoids can be shrunk through a special injection that stops the local circulation. Usually three treatments, one every 4-6 weeks are necessary. The treatment is done ambulatorily.
Rubber band ligation:
Inner hemorrhoids can be treated with a rubber band ligation. Via rectoscopy (link), a rubber band is placed around the hemorrhoids. The hemorrhoids will then shrink and fall off a few days later.
Usually, 3-5 sessions with an interval of 4-6 weeks are necessary.
Surgical measures
The classical surgery is to remove the hemorrhoids. The downside to this though is the remaining wound in a very sensitive region. Those procedures are usually performed under general anesthesia or epidural anesthesia.
New ways of Hemorrhoid surgery
Stapled hemorrhoidectomy:
This method brings hemorrhoids back to their original place, through shortening the hemorrhoidal tissue with a stapler, without incisions at the sensitive anus.
Transanal hemorrhoidal dearterialization:
After locating the superior rectal arteries via ultrasound, a suture ligation is performed. This procedure can be done under conscious sedation, with an additional medication of Dormicum.
There is no risk of fecal incontinence.
Risks and long-term results:
After the classic surgery, pain during bowel movement is common in the first few days. Very rarely, tightness of the sphincter, impaired control over bowel movement or newly enlarged hemorrhoids can occur.
HEMORRHOIDS
Hemorrhoids are blood filled cushions under the skin in the lower rectum, that help with stool control. Every human has hemorrhoids. Only when they are swollen or inflamed the become a disease.
Symptoms can be a light red bleeding from the anus, itchiness, burning, wetness or secretion from the anus or a feeling of pressure. Seldomly they also come with pain.
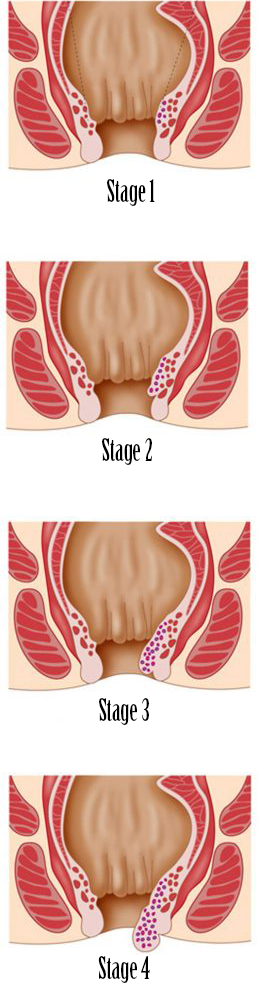
Hemorrhoids are divided into 4 stages:
Stage 1: The hemorrhoids cannot be felt but seen with the proctoscope.
Stage 2: When pushing, the hemorrhoids can shortly bulge out of the anal canal but return on their own.
Stage 3: The hemorrhoids come out of the anal canal but can be pushed back with a finger.
Stage 4: The hemorrhoids are permanently outside of the anus and cannot be pushed back in.
We treat each patient according to their individual medical needs. In stage 1 and 2 we recommend dietary changes, stool regulation, as well as suppositories and salves. Patients with stage 2 hemorrhoids can additionally have a rubber band ligation and/or sclerotherapy.
In stage 3 and 4, a surgery is necessary. There are several types of surgery: removing the hemorrhoids, stapled hemorrhoidectomy and the trans anal hemorrhoidal ligation.